Historical fire pits were sometimes constructed in the ground, in caves, or at the middle of a hut or dwelling. Evidence of ancient, man-made flames is present on all five inhabited continents. The drawback of early indoor flame pits was that they generated hazardous or irritating smoke inside the dwelling.Fire pits developed into elevated hearths in buildings, but ventilation smoke relied on open windows or holes in roofs. The great hall typically needed a centrally located hearth, where a open fire burnt with all the smoke rising to the port in the roof. Louvers were developed during the Middle Ages to allow the roof vents to be covered so snow and rain wouldn't enter.
Also during the Middle Ages, smoke canopies were devised to stop smoke from spreading through a room and vent it outside via a ceiling or wall. These can be placed against stone walls, instead of taking up the center of the space, and this enabled smaller rooms to be warmed.Chimneys were devised in northern Europe from the 11th or 12th centuries and largely fixed the problem of fumes, more reliably venting smoke out. They made it possible to give the fireplace a draft, and made it possible to put fireplaces in multiple rooms in buildings conveniently. They didn't come into general usage immediately, however, since they were expensive to build and maintain.In 1678 Prince Rupert, nephew of Charles I, increased the grate of the fireplace, improving the venting and airflow system. The 18th century saw two major developments in the history of fireplaces. Benjamin Franklin developed a convection chamber for the fireplace that greatly improved the efficacy of fireplaces and wood stoves. He also improved the airflow by pulling air from a basement and venting out a longer area on top. At the later 18th century, Count Rumford made a fireplace using a tall, shallow firebox which was better at drawing the smoke up and from the construction. The shallow design improved greatly the amount of radiant heat projected into the room. Rumford's layout is the basis for modern kitchens.
The Aesthetic movement of the 1870s and 1880s took on a more conventional spectra based on stone and also deflected unnecessary ornamentation. Rather it depended on simple designs with small unnecessary ornamentation. In the 1890s the Aesthetic movement gave way into the Arts and Crafts movement, in which the emphasis was placed on supplying quality gems. Stone fireplaces at this time have been a sign of prosperity, which to some degree is still the notion today.A fireplace is a structure made from brick, stone or metal designed to contain a fire. Fireplaces are utilized for the relaxing ambiance that they create and for heating a space. Modern fireplaces vary in heat efficiency, based on the design.Historically they were utilized for heating a dwelling, cooking, and heating water for domestic and laundry uses. A fireplace might have the following: a foundation, a hearth, a firebox, a mantelpiece; a chimney crane (utilized in kitchen and laundry fireplaces), a grate, a lintel, a lintel bar, home overmantel, a damper, a smoke chamber, a neck, a flue, and a chimney filter or afterburner.
Related Images with Fireplace Chimney Repair San Diego County
HeatShield® Chimney Relining Chimney Liner Repair CT Chimney Sweeps
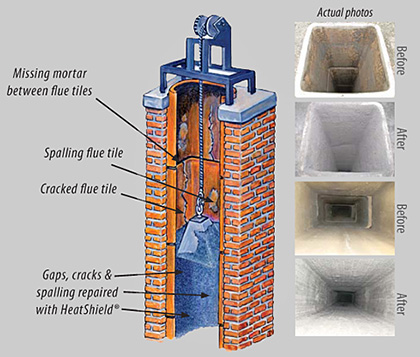
On the exterior there is often a corbeled brick crown, where the projecting courses of brick function as a drip course to keep rainwater from running down the exterior walls. A hood, cap, or shroud serves to keep rainwater out of the exterior of the chimney; rain in the chimney is a much larger difficulty in chimneys lined with impervious flue tiles or metal liners than with the traditional masonry chimney, that soaks up all but the rain. A few chimneys have a spark arrestor incorporated into the crown or cap.
Organizations like the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the Washington Department of Ecology warn that, according to various studies, fireplaces could pose a substantial health threat. The EPA writes"Smoke may smell good, but it's not good for you.Kinds of fireplacesArtificial fireplaces are made with sheet metal or glass flame boxes.Electric fireplaces could be built-in replacements for gas or wood or retrofit with log inserts or electric fireboxes.A few kinds are, wall mounted electric fireplaces, electric fireplace stoves, electrical mantel fireplaces and fixed or free standing electric fireplaces.
Ventless Fireplaces (duct free/room-venting fireplaces) are fueled by gel, liquid propane, bottled gas or natural gas. In the USA, some states and local businesses have laws restricting these types of fireplaces. Additionally, there are air quality control issues because of the amount of moisture that they discharge in the room air, and oxygen sensor and carbon dioxide sensors are safety essentials. Direct vent fireplaces are fueled by either liquid propane or natural gas. They are totally sealed from the area that's heated, and port all exhaust gasses into the outside of the structure.
Fireplace Wikipedia
Over time, the intent behind fireplaces has changed from one of necessity to one of interest. Early ones were more fire pits than contemporary fireplaces. They were used for warmth on cold days and nights, as well as for cooking. They also functioned as a gathering place inside the home. These fire pits were generally centered within a space, allowing more people to gather around it.
Poker Damper Operation YouTube

How to Repair a Flue Damper eHow

Many defects were found in ancient fireplace designs. The most renowned fireplace designers of this time were the Adam Brothers. They perfected a kind of fireplace design that has been used for generations. It had been smaller, more brightly colored, with a emphasis on the quality of the substances used in their construction, instead of their dimensions.
By the 1800s most new fireplaces were composed of two components, the surround and the add. The encircle comprised of the mantlepiece and sides affirms, usually in wood, granite or marble. The insert was fire burnt, and was constructed of cast iron frequently backed with decorative tiles. In addition to providing heat, the fireplaces of the Victorian age were thought to bring a cozy ambiance into homes.How to Repair a Flue Damper eHow Video
Some fireplace units include a blower that transports more of the fireplace's heat to the atmosphere via convection, resulting in a more evenly heated space and a lower heating load. Fireplace efficiency can also be enhanced with the use of a fireback, a piece of metal which sits behind the fire and reflects heat back into the room. Firebacks are traditionally made from cast iron, but are also manufactured from stainless steel. Efficiency is a complex concept though with open hearth fireplaces. Most efficacy tests consider just the impact of heating of the atmosphere. An open fireplace is not, and never was, designed to heat the air. A fireplace with a fireback is a radiant heater, and has done so as the 15th century. The ideal method to estimate the output signal of a fireplace is if you detect you are turning the thermostat up or down.
Most older fireplaces have a relatively low efficiency rating. Standard, modern, wood-burning masonry fireplaces though have an efficiency rating of at least 80% (legal minimum necessity such as in Salzburg/Austria). To boost efficiency, fireplaces may also be modified by adding special heavy fireboxes designed to burn much cleaner and can reach efficiencies as large as 80% in heating the air. These altered fireplaces are usually equipped with a large fire window, allowing an efficient heating system in two phases. During the first phase the first heat is provided through a large glass window while the flame is burning. In this time period the construction, built of refractory bricks, absorbs the heat. This heat is then equally radiated for many hours during the next phase. Masonry fireplaces without a glass fire window just provide heat radiated from its surface. Depending on temperatures 1 to 2 daily firings are enough to ensure a constant room temperature.fireplace flue
No comments:
Post a Comment